If you're stuck with a USB drive or SD card that can't be format or the disk is write protected. You'll find that an USB flash drive or SD card will refuse to format and Windows will tell you that it is write protected, ever through there is no format option. Sometime the things get out of control and you can read the files which are already stored on the drive, but you can't delete them.
Formatting a USB drive is not different than formatting any other drive. Here are some simple methods you can try to remove write protection and erase or format it.
Formatting a USB drive is not different than formatting any other drive. Here are some simple methods you can try to remove write protection and erase or format it.
Difference between FAT32, exFAT and NTFS
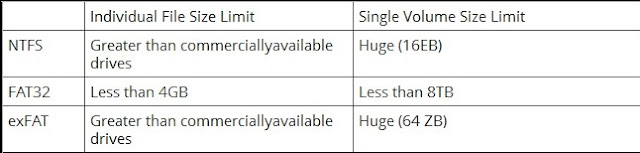
1. FAT32 is the oldest file system and introduced all the way back in Windows 95 to replace the older FAT16 file system. Most of the Flash drive will often come formatted with FAT32 for maximum compatibility across not just modern computers but other devices like game consoles and anything with a USB port. There are some limitation like Individual files on a FAT32 drive can't be over 4 GB in size and lacks the permission and other security features built into the more modern NTFS file system.
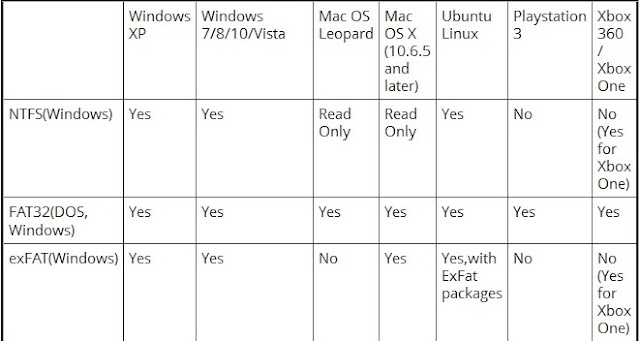
Compatibility: Works with all versions of Windows, Mac, Linux, game consoles, and practically anything with a USB port.
Limits: 4 GB maximum file size, 8 TB maximum partition size.
Ideal Use: Use it on removable drives for maximum compatibility with the widest range of devices, assuming you don’t have any files 4 GB or larger in size.
Limits: 4 GB maximum file size, 8 TB maximum partition size.
Ideal Use: Use it on removable drives for maximum compatibility with the widest range of devices, assuming you don’t have any files 4 GB or larger in size.
2. NTFS file system was introduced in the consumer version of Windows XP and packed with modern features like support file permission for security, a change journal that can help quickly recover errors if your computer crashes, shadow copies for backups, encryption, disk quota limits, hard links etc.
Compatibility: Works with all versions of Windows, but read-only with Mac by default, and may be read-only by default with some Linux distributions. Other devices — with the exception of Microsoft’s Xbox One — probably won’t support NTFS.
Limits: No realistic file-size or partition size limits.
Ideal Use: Use it for your Windows system drive and other internal drives that will just be used with Windows.
Limits: No realistic file-size or partition size limits.
Ideal Use: Use it for your Windows system drive and other internal drives that will just be used with Windows.
3. exFAT was introduced in 2006 and was added to older versions of Windows with updates to Windows XP and Windows Vista. It's a file system optimized for flash drives and has very large file size. You can store files that are larger than 4 GB apiece on a flash drive or SD card. exFAT is a strict upgrade over FAT32, and should be the best choice for external drives where you want a lightweight file system without FAT32’s file size limits.Compatibility: Works with all versions of Windows and modern versions of Mac OS X, but requires additional software on Linux. More devices support exFAT than support NTFS, but some — particularly older ones — may only support FAT32.
Limits: No realistic file-size or partition-size limits.
Ideal Use: Use it for USB flash drives and other external drives, especially if you need files of over 4 GB in size. Assuming every device you want to use the drive with supports exFAT, you should format your device with exFAT instead of FAT32.
Limits: No realistic file-size or partition-size limits.
Ideal Use: Use it for USB flash drives and other external drives, especially if you need files of over 4 GB in size. Assuming every device you want to use the drive with supports exFAT, you should format your device with exFAT instead of FAT32.
How to Format a Write Protected USB stick
In any version of Windows from XP onwards, run Regedit.exe and Navigate to the following key
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\StorageDevicePolicies
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\StorageDevicePolicies
Double-click on the WriteProtect value in the right-hand pane of Regedit.exe. Change the Value data from 1 to 0 and click OK to save the change. Close Regedit and restart your computer. Connect your USB drive again, and you should find it is no longer write protected. You can now format the drive as normal by right-clicking on it in My Computer and choosing Format.
You can also use Diskpart to remove write protection from USB stick